See how Business Intelligence Architecture empowers teams to make informed choices using reliable, real-time data insights.
That’s exactly what Business Intelligence Architecture offers you. It’s the backbone that supports data storage, integration, and reporting, helping you make smarter decisions faster. You’ll discover how a well-designed BI architecture can transform your data into a powerful tool for growth, efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Ready to unlock the full potential of your business data? Keep reading to learn how to build a BI architecture that works for you.
Credit: www.altexsoft.com
Bi Architecture Fundamentals
Business Intelligence (BI) architecture forms the backbone of effective data analysis and reporting. It organizes raw data into meaningful insights that help businesses make informed decisions. Understanding BI architecture fundamentals is essential for designing systems that handle data efficiently and deliver accurate results.
The architecture includes various layers and components working together. Each part plays a crucial role in managing data flow, storage, and accessibility. Clear knowledge of these fundamentals helps build robust BI systems that meet business needs.
Core Components
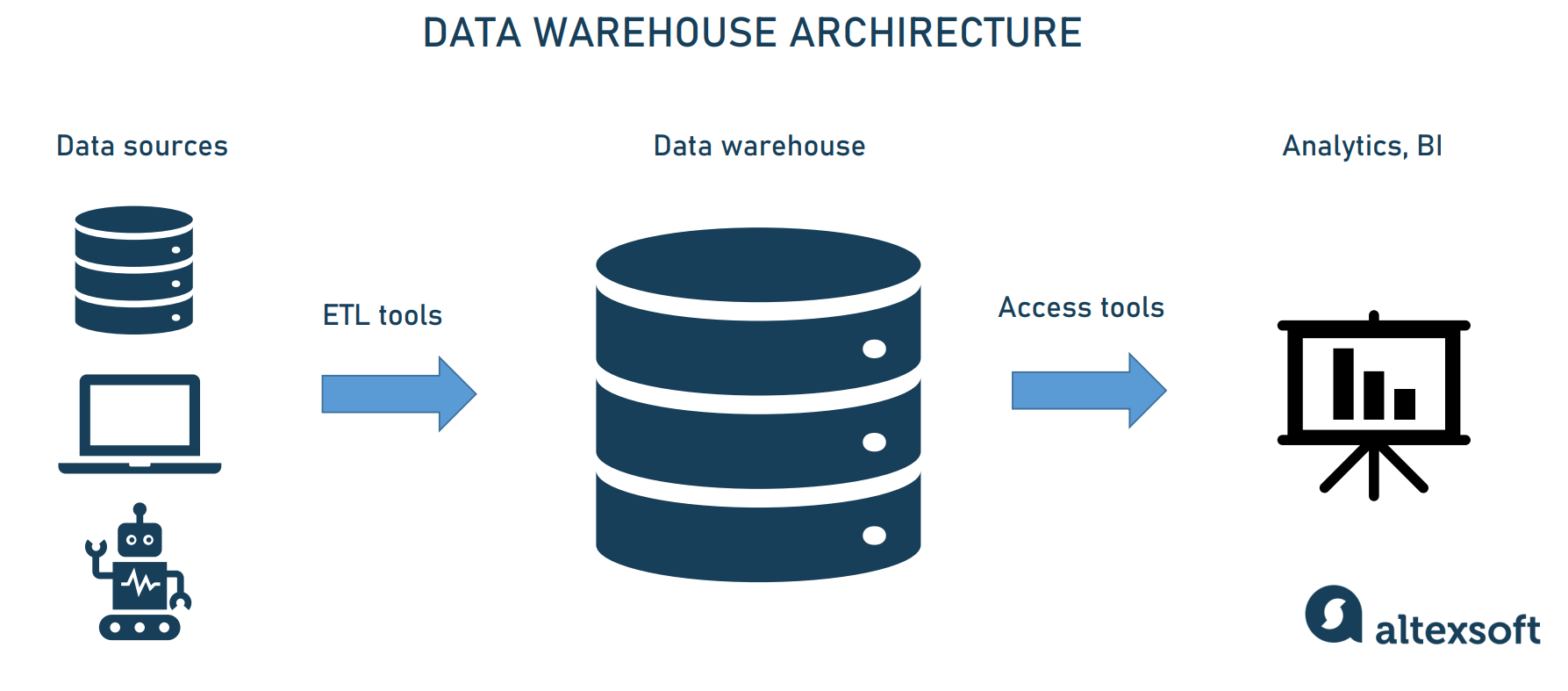
BI architecture consists of key components that process and deliver data insights. These include data sources, ETL tools, data storage, and reporting platforms. Data sources collect raw information from various systems.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools clean and prepare this data for analysis. Data storage holds the processed data securely, ready for use. Reporting tools then visualize the data, making it easy to understand and act upon.
Data Warehouses And Lakes
Data warehouses store structured data from multiple sources. They organize data into tables optimized for fast queries and reporting. Data lakes hold large volumes of raw and unstructured data.
Lakes allow storing diverse data types without strict formatting. Both warehouses and lakes are vital for comprehensive data management. Warehouses support detailed analysis, while lakes enable flexible data exploration.
Data Models And Metadata
Data models define how data is organized and related within the system. They create a clear structure that supports efficient querying and reporting. Metadata provides information about the data’s origin, format, and usage.
This helps users understand data context and trust its accuracy. Proper data modeling and metadata management improve system performance and data governance. They ensure users find the right data quickly and use it correctly.

Credit: www.tutorialspoint.com
Roles Of A Bi Architect
A Business Intelligence (BI) Architect plays a crucial role in shaping how organizations use data. They build systems that turn raw data into useful information. This helps businesses make smarter and faster decisions. BI Architects focus on designing the structure of BI tools, ensuring smooth data flow, and creating reports that are easy to understand.
Their work involves both technical skills and communication. They connect business needs with technology solutions. This role requires a clear vision of data management and the ability to lead teams.
System Design And Development
BI Architects create the blueprint for BI systems. They design data warehouses and data lakes to store large amounts of data. They develop data models that organize data efficiently. This design supports easy access and fast processing. Architects also ensure the system handles data securely and accurately. They build metadata layers that help users find the right information. System development includes integrating multiple data sources into one platform.
Stakeholder Collaboration
BI Architects work closely with business leaders and users. They gather requirements to understand what data is needed. They translate these needs into technical plans. Clear communication helps avoid misunderstandings. Architects make sure BI tools meet business goals. They also train users on how to use BI reports. This collaboration ensures the system provides real value. It helps align technology with business strategies.
Technical Leadership
BI Architects lead the technical team building BI solutions. They set standards for coding and data quality. They guide developers and analysts during the project. Architects solve complex technical problems that arise. They monitor system performance and suggest improvements. Leadership includes planning for future growth and scalability. Architects ensure the BI platform adapts to new business demands. They act as a bridge between business and technology teams.
Building The Data Layer
The data layer forms the foundation of any Business Intelligence (BI) architecture. It collects, stores, and prepares data for analysis. Building this layer requires careful planning to ensure data is accessible and reliable. A strong data layer supports accurate reporting and insightful decision-making.
Integration Of Data Sources
Data comes from many places such as databases, cloud services, and applications. Combining these sources into one system is key. This process involves extracting data, transforming it to a common format, and loading it into a central storage. Proper integration allows for a unified view of business information.
Ensuring Data Accuracy
Accurate data is critical for trustworthy insights. Data must be cleaned and validated before use. Errors, duplicates, and missing values can cause wrong conclusions. Regular checks and automated rules help maintain data quality. Accurate data builds confidence in BI reports.
Metadata Management
Metadata describes data, giving context and meaning. It helps users understand what data represents and where it comes from. Managing metadata includes documenting data definitions, sources, and usage rules. Good metadata management improves data discovery and governance.
Data Governance And Security
Data governance and security form the backbone of any robust Business Intelligence (BI) architecture. These elements ensure that data is reliable, accessible only to authorized users, and protected from threats. Proper governance defines who manages data and how it is used. Strong security measures guard sensitive information against breaches and misuse.
Effective data governance and security boost trust in BI systems. They help organizations comply with regulations and protect their reputation. The following sections explore key aspects of governance and security in BI architecture.
Access Controls
Access controls regulate who can view or modify data in BI systems. They use roles, permissions, and authentication methods to limit data access. This prevents unauthorized users from seeing confidential information.
Role-based access control (RBAC) assigns users specific rights based on their job functions. Multi-factor authentication adds an extra security layer by requiring multiple proofs of identity. Audit trails track user activity to detect suspicious behavior early.
Data Consistency
Data consistency ensures that information remains accurate and uniform across all BI components. It avoids errors caused by conflicting or outdated data. Consistent data improves decision-making and reporting reliability.
Data validation rules check incoming data for correctness before storage. Synchronization processes keep data updated between different sources and systems. Regular audits identify and fix inconsistencies promptly.
Security Best Practices
Implementing security best practices protects BI architecture from internal and external threats. Encrypting data both at rest and in transit safeguards it from interception. Firewalls and intrusion detection systems block unauthorized access attempts.
Regular security training for users raises awareness of potential risks. Updating software patches closes vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them. Backups ensure data recovery in case of accidental loss or cyberattacks.
Optimizing Performance
Optimizing performance is crucial for any Business Intelligence (BI) architecture. It ensures data processes run smoothly and deliver quick, accurate insights. Efficient BI systems reduce delays and improve user satisfaction. This section explores key methods to boost BI performance.
System Monitoring
System monitoring tracks the health and activity of BI components. It helps detect bottlenecks early and avoid downtime. Monitoring tools collect data on server load, query times, and network traffic. Alerts notify teams about unusual behavior or failures. Regular checks maintain smooth data flow and system reliability.
Scalability Strategies
Scalability allows BI systems to handle growing data volumes and users. Horizontal scaling adds more servers to share the workload. Vertical scaling upgrades existing hardware for better power. Cloud services offer flexible, on-demand resources. Proper scalability keeps performance stable despite growth.
Resource Utilization
Efficient resource use maximizes hardware and software capabilities. Balancing CPU, memory, and storage prevents overloads. Load balancing spreads tasks evenly across servers. Optimizing database queries reduces processing time. Good resource management lowers costs and speeds up BI operations.
Selecting Bi Tools And Standards
Selecting the right BI tools and standards is crucial for a strong Business Intelligence Architecture. These choices shape how data is collected, processed, and analyzed. Proper selection ensures accuracy, speed, and usability of BI systems.
This section covers how to evaluate BI products, implement standards, and align tools with business goals. Each step helps build a reliable BI environment that supports smart decision-making.
Evaluating Bi Products
Start by reviewing product features and capabilities. Check how well the tool integrates with existing systems. Look for ease of use and customization options. Consider data security and compliance features. Assess vendor support and update frequency. Test the tool with real business data for practical insights. Compare pricing models and total cost of ownership. Select products that fit current and future needs.
Implementing Standards
Establish clear guidelines for data quality and consistency. Use common data formats and naming conventions. Define rules for data access and user permissions. Ensure compliance with industry regulations and policies. Apply standards for report design and visualization. Maintain documentation for all BI processes. Train teams on these standards to avoid errors. Regularly review and update standards as technology evolves.
Aligning Tools With Business Goals
Choose BI tools that support key business objectives. Focus on solutions that improve decision speed and accuracy. Ensure tools provide relevant insights to all departments. Align BI capabilities with strategic priorities. Avoid tools with unnecessary features that add complexity. Involve business leaders in the selection process. Measure tool performance against business outcomes. Adjust tool use to stay aligned with changing goals.
Essential Skills For Bi Architects
Business Intelligence (BI) architects need a diverse skill set to build effective BI systems. These skills help them turn raw data into clear, useful insights. A BI architect combines technical knowledge with business understanding. This balance ensures data supports smart decisions and drives growth.
Strong skills make BI architects valuable team members. They help design systems that handle data efficiently and meet business needs. Below are the key skills every BI architect should have.
Technical Expertise
BI architects must know databases, data warehouses, and ETL tools well. They work with data modeling, SQL, and BI platforms like Power BI or Tableau. Understanding cloud services such as AWS or Azure is also important. Technical skills ensure the BI system runs smoothly and scales with business growth.
Analytical Thinking
Analyzing complex data is central to BI architecture. Architects break down problems and find patterns in data. They identify trends and spot data quality issues. Analytical thinking helps them design solutions that deliver accurate, timely insights. It also supports continuous improvement of BI systems.
Effective Communication
BI architects explain technical ideas clearly to business teams. They translate business needs into technical requirements. Good communication helps avoid misunderstandings and keeps projects on track. Architects also train users and support decision-makers with easy-to-understand reports.
Business Domain Knowledge
Knowing the business industry improves BI architecture outcomes. Architects understand key processes and challenges in sectors like finance, healthcare, or retail. This insight helps them design relevant data models and reports. Business knowledge ensures BI tools add real value to the company.
Career Path And Education
Building a career in Business Intelligence Architecture requires a solid educational foundation and continuous learning. This field blends data analysis, technology, and business strategy. Professionals must understand data systems and how to turn data into useful insights. Education and training play key roles in preparing for this dynamic career path.
Academic Background
A bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, or business analytics is common. Some roles may require a master’s degree for advanced knowledge. Courses in database management, programming, and data modeling help build relevant skills. Understanding statistics and business fundamentals supports better decision-making.
Certifications And Training
Certifications boost expertise and credibility. Popular options include Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate and Certified Business Intelligence Professional (CBIP). Training in tools like SQL, Tableau, and Power BI is valuable. Online courses and workshops offer flexible learning paths. Regularly updating skills keeps professionals competitive.
Professional Growth
Starting as a data analyst or developer builds practical experience. Moving into roles like BI developer or data architect follows naturally. Leadership positions such as BI manager or director become attainable with experience. Networking and mentorship accelerate career advancement. Staying current with industry trends ensures long-term success.
Read More : Dmarc Report Lifetime Deal: 5 Reasons It’s the Best Email Security Investment
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Role Of A Business Intelligence Architect?
A business intelligence architect designs and implements BI systems to transform data into actionable insights. They develop data models, warehouses, and reporting tools, ensure data accuracy and security, optimize system performance, and guide teams to meet business analytics needs effectively.
What Is A Five Layered Business Intelligence Architecture?
A five-layered business intelligence architecture includes data sources, data integration, data storage, data analysis, and presentation layers. It organizes data flow from raw inputs to actionable insights. This structure ensures efficient data management, accurate reporting, and supports informed business decisions.
What Are The 4 Concepts Of Business Intelligence?
The four concepts of business intelligence are data collection, data integration, data analysis, and data presentation. These concepts enable informed decision-making and improve business performance.
Is Business Intelligence The Same As Etl?
Business intelligence (BI) analyzes and visualizes data for decision-making. ETL extracts, transforms, and loads data into systems. ETL is a part of BI but not the same. BI uses ETL to prepare data but includes reporting, analysis, and insights beyond ETL processes.
Conclusion
A strong Business Intelligence Architecture helps companies use data wisely. It builds a clear path from raw data to useful insights. Good design supports faster decisions and better results. Teams work closely to keep data accurate and secure. Regular updates keep the system running smoothly and efficiently.
Overall, a well-planned BI architecture drives smarter business choices every day.



